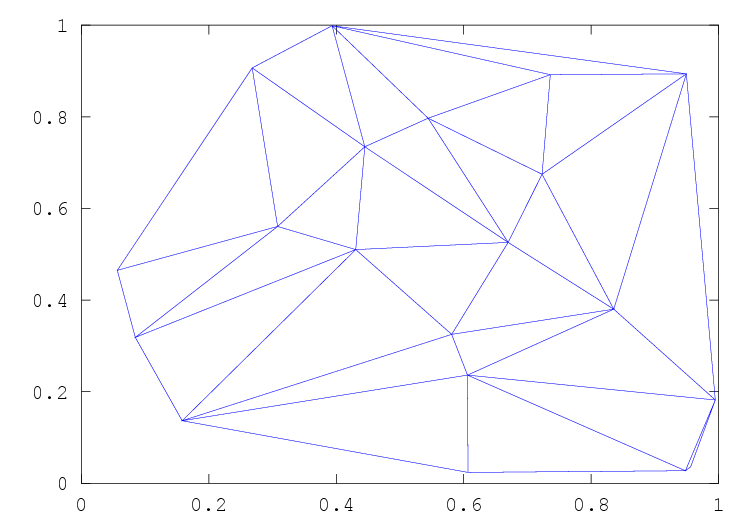
Figure 30.2: Delaunay triangulation of a random set of points
Octave has the functions triplot, trimesh, and trisurf
to plot the Delaunay triangulation of a 2-dimensional set of points.
Plot a triangular mesh in 2D. The variable tri is the triangular meshing of the points
(x,y)which is returned fromdelaunay. If given, linespec determines the properties to use for the lines.The optional return value h is a graphics handle to the created plot.
Plot a triangular mesh in 3D. The variable tri is the triangular meshing of the points
(x,y)which is returned fromdelaunay. The variable z is value at the point(x,y).The optional return value h is a graphics handle to the created plot.
Plot a triangular surface in 3D. The variable tri is the triangular meshing of the points
(x,y)which is returned fromdelaunay. The variable z is value at the point(x,y).The optional return value h is a graphics handle to the created plot.
The difference between triplot, and trimesh or triplot,
is that the former only plots the 2-dimensional triangulation itself, whereas
the second two plot the value of a function f (x, y). An
example of the use of the triplot function is
rand ("state", 2)
x = rand (20, 1);
y = rand (20, 1);
tri = delaunay (x, y);
triplot (tri, x, y);
which plots the Delaunay triangulation of a set of random points in 2-dimensions. The output of the above can be seen in fig:triplot.